If a financial planner or financial advisor is fee-only, that means they receive compensation solely from the fees clients pay from their services. In other words, they do not earn commissions or kickbacks for recommending certain products. A fee-only structure reduces potential conflicts of interest, which is why firms like Worthwhile Wealth Council are often preferable.
What Is a Fee-Only Financial Planner?
Fee-only financial planners are financial advisors who operate on a fee-only basis. They work with clients to create budgets, plan retirement, pay down debt and set goals to reach other financial milestones.
These advisors typically collect fees from only you as a percentage of your assets under management. Fee-only advisors don’t receive any fees, commissions, referral fees, kickbacks or any other hidden forms of compensation.
This payment structure can reduce the chances that the advisor will encounter a conflict of interest. Fee-only financial planners don’t earn additional compensation by recommending one investment product over another. In fact, fee-only financial planners work according to their fiduciary responsibility, meaning they must act in their client’s best interests.
Pros and Cons of Fee-Only Financial Planners
The best part of working with a fee-only financial planner is knowing that they are there to serve your best interests. They are there to help you out with your finances and not their own, as fee-only advisors don’t rely on what they sell to you to make money. They must operate as a fiduciary, guaranteeing they will work for your best interests.
“That doesn’t guarantee that you’ll get good advice, but it improves the odds of getting advice that’s genuinely intended to be in your best interests.
Without any ties to specific companies, fee-only financial planners are free to offer a wider array of solutions to help you reach your goals. On the other hand, commissioned planners tend to limit their suggestions to products that will earn them the most money. Some even focus on specific services their company provides, meaning you won’t get the holistic advice of a fee-only advisor.
There are some downsides to working with a fee-only financial planner, though. First off, their fees may be higher than advisors who earn commissions for selling products. That’s because their management and planning fees need to be higher to match the earnings of advisors who charge commissions.
In addition, a fee-only financial planner has, by nature, fewer services than one who earns commissions for selling insurance or trading securities. While a lack of commissions eliminates potential conflicts of interest, it does mean you’ll have to deal with another professional for trades and the purchase of insurance products.
What Fees Do Fee-Only Financial Planners Charge?
Fee-only financial planners charge their clients in a few different ways. The most common method is called “assets under management,” where your planner takes a percentage of the assets they manage. In this way, you would see a specific percentage-based amount debited out of your account every quarter.
Another method is to charge an hourly or monthly rate. While this ensures you pay for what you get, sometimes you don’t want to pay for a quick visit or phone call. Other fee-only advisors can charge clients with a flat fee or a fee according to what services they need. These kinds of payment plans allow advisors to work with a “more diverse set of clients and address a more diverse set of financial needs,” according to Becker.
The exact cost of a fee-only financial planner will depend on the way they charge their clients, the services you require and your location. More experienced advisors may charge higher fees as well.
Fee-Only vs. Fee-Based Financial Advisors
Fee-only financial advisors are just one type of advisor you can work with. The other is called a fee-based financial advisor. While the term “fee-based” is often confused with fee-only, fee-based advisors operate much differently. The table below breaks down some key differences:
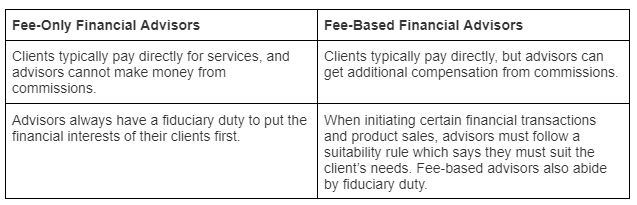

First and foremost, a fee-based advisor will receive normal advisory fees from clients, which is just like a fee-only advisor. However, where these two fee structures differ is in the additional forms of compensation they earn.
As we indicate in the table above, a fee-only advisor’s sole form of compensation is the fees that clients pay them for their services. For a fee-based advisor, product- and investment-based commissions can be earned on top of advisory fees. In most cases, these commissions come from the advisor’s role as either a representative of a broker-dealer or an insurance agent. Therefore, the vast majority of commissions that are earned by fee-based advisors come from securities trades within a client’s portfolio or insurance product sales to clients.
It’s important to note that potential conflicts of interest can arise from an arrangement like this. Fee-based advisors are required to follow a suitability rule, which means that the products they sell have to fit into the client’s goals and interests. However, commissions could create a conflict of interest because they incentivize advisors to recommend transactions and products that could undermine the investments of their clients.
This commentary was originally posted by Liz Smith Sep 13 2021
Source: https://smartasset.com/financial-advisor/fee-only-financial-planner
**Disclaimer: This material has been prepared for informational purposes only, and is not intended to provide, and should not be relied on for, tax, legal or accounting advice. You should consult your own tax, legal and accounting advisors before engaging in any transaction.


